More and more car systems are equipped with a variety of MEMS inertial sensors to enhance the reliability of the car and improve the safety of the driver. Lower prices, more reliable equipment, and higher-end technologies have realized many ideal functions of automobiles and are becoming more and more popular.
The application of inertial sensors in automotive systems is ubiquitous. Some may be commonplace, and some may seem familiar. Although some cutting-edge technologies are only present in high-end cars, they will gradually be adapted to all models in the future and become standard configurations.
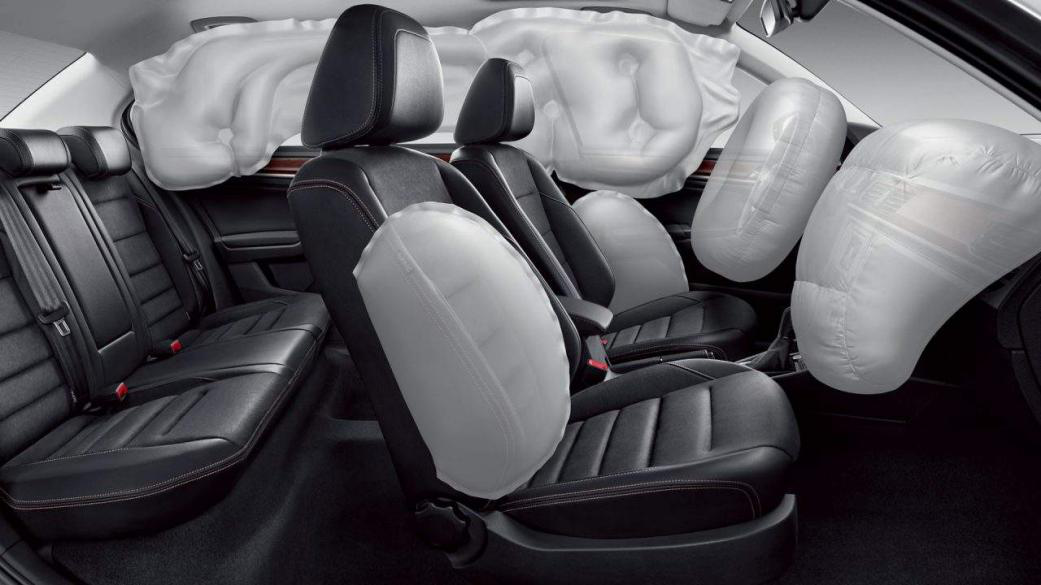
1. Rollover detection
In the rollover detection system, the inertial sensor reads the main data of the vehicle's roll angle, roll rate, acceleration, etc., detects whether the vehicle is rollover and triggers the airbag device to protect the occupants. In recent years, large-scale vehicle accidents have occurred frequently. Because these vehicles are bulky, have a high center of gravity, and often load bulk goods, their center of gravity is unstable and they are more prone to rollover. Vehicles are in different environmental conditions during actual driving, and have extremely high requirements on the stability and accuracy of inertial sensors, and there are many models, requiring a set of devices that meet the standards and adapt to the vehicle system.

2. Inertial navigation
The construction of modern urban roads is developing rapidly. Navigation ensures that the majority of drivers can shuttle through unfamiliar or complex road systems. The built-in navigation system of the vehicle uses global navigation satellite systems, path planning, and inertial navigation systems to obtain road information in real time. The inertial sensor is added to the navigation system to complement and perfect the single satellite navigation mode. Rows of tall buildings, deserted fields, weak or unstable satellite system signals or even loss, inertial sensors can still estimate the displacement based on the last updated position information direction.
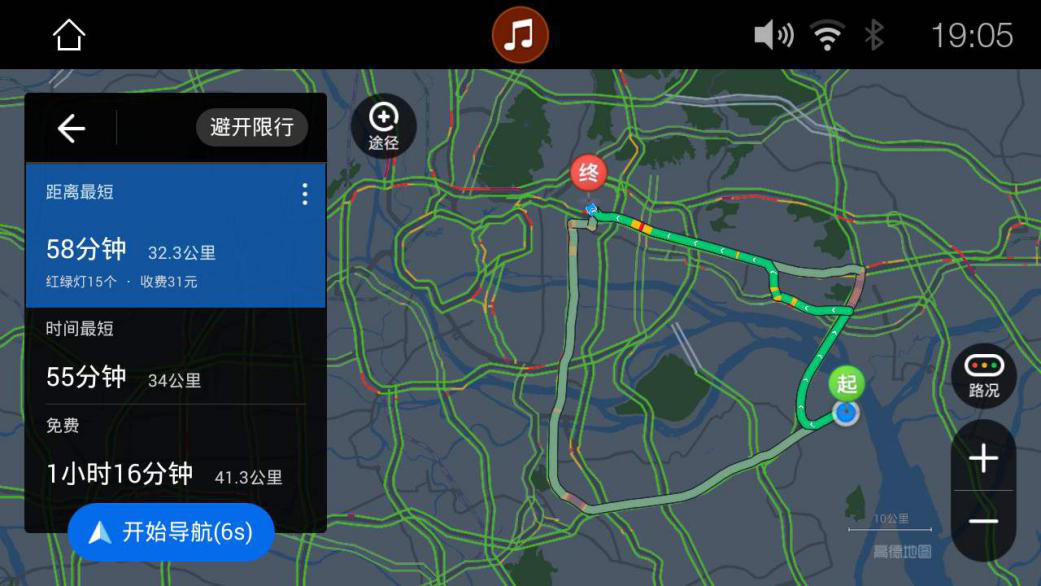
3. Assisted and autonomous driving
Inertial sensors are combined with radar, image capture and other perception systems to realize distance control, vehicle speed adjustment, lane change, and emergency braking. The traditional cruise function is to maintain a constant speed, but the speed of the surrounding vehicles and lanes will change at any time, and they still need to switch continuously. The active vehicle distance control cruise radar measures the distance and can adjust the vehicle speed as needed to maintain a safe distance from other vehicles. Inertial sensors perform route prediction and planning, and also assist cruise. When the vehicle is uphill, the inertial sensor detects the tilt angle and determines the correction force to be applied to prevent the vehicle from slipping backward, effectively improving driving skills and personnel safety. Similarly, inertial sensors use cameras, radars and lasers to assist driving. Perceive the environment where the vehicle belongs, record, analyze and predict driving habits, combine map navigation and vision systems to plan driving paths to realize autonomous driving. In the autonomous driving experiments conducted in recent years, it is still easy to do in a relatively simple driving environment.


 +86 189 2129 2620
+86 189 2129 2620
+86 176 0611 8008 sales@bwsensing.com
sales@bwsensing.com














